Appeal in place – Vietnam is well-positioned to continue hosting a vibrant M&A space
The article was originally published in the September 2021 issue of Vietnam Economic Times
Huong Trinh
Managing Director, Head of Ho Chi Minh, BDA Partners
Despite Vietnam experiencing its fourth wave of Covid-19, merger and acquisition (M&A) activities will continue to remain strong. Since the beginning of this year, we at BDA Ho Chi Minh City have seen strong interest from large regional PEs (private equity firms) looking for sizable transactions. We are also observing strong demand for growth capital and exits from both founder-backed and private equity-owned companies, evidenced by numerous current live deals and strong pipelines/opportunities for 2021.
Vietnam’s macroeconomic fundamentals remain strong. In the International Monetary Fund (IMF)’s revised forecast released in July, the country is still on track to remain the fastest-growing economy in Southeast Asia this year, with projected growth of 6.5 percent. Vietnam also has one of the fastest-growing middle-class populations, with rising discretionary spending power, leading to high pent-up demand for goods and services that will contribute to economic recovery as the country opens up again later this year.
Key industries predicted to grow strongly
In general, Vietnam’s economy has remained resilient and maintained good momentum for growth across industries despite the recent surge of Covid-19. In addition to consumer and retail which has always been one of the most active sectors in Vietnam and is expected to rebound strongly in 2022 thanks to the recovery of consumer confidence, the following sectors have been attracting a lot of interest.
We believe that IT & Technology and especially the internet-related segment will achieve the strongest growth in Vietnam, and that there will be a strong pipeline of opportunities for the sector in 2021 and upcoming years. Difficulties caused by the pandemic have driven growth in demand across all industries for technology-related services and digital solutions that help businesses function normally. In a post-pandemic world, there will be a continued push for swift digitalization, and M&As will be the fastest way for businesses to achieve this goal. Also, Vietnam’s internet economy has been growing rapidly during Covid-19, and we expect this trend to continue as there have been long-term changes to consumer habits and dynamics. The pandemic, for all its negative impacts on health, society, and economy, is propelling the growth of e-commerce and digital finance in Vietnam, paving the way for the country to fulfill its digital potential. According to the Ministry of Industry and Trade, Vietnam’s e-commerce market grew 18 percent year-on-year in 2020 to $11.8 billion, while traffic on e-commerce platforms was 150 percent higher than in 2019.
Pharmaceuticals is an industry that has attracted a lot of interest from foreign investors in recent years, with notable transactions including Taisho’s acquisition of a majority stake in DHG Pharma and SK’s recent investment in Imexpharm. According to BMI Research, Vietnam’s pharmaceutical industry could reach $7.7 billion in 2021 and $16.1 billion in 2026. A growing middle class, urbanization, and a young population are driving domestic demand for all aspects of healthcare, including expenditures on pharmaceuticals. As a defensive sector, pharmaceuticals will continue to achieve strong growth as Vietnam transitions out of the pandemic period. The industry is set to benefit greatly from the government’s national strategy to promote domestic manufacturing. To compete with imports, M&As with foreign strategic investors will continue to be crucial for local manufacturers, enabling them to meet global pharmaceutical standards through transfers of technology, R&D, and management expertise.
Renewable energy has also become an interesting sector for M&A activity in Vietnam over recent years, and we expect deal flow to resume as the country gradually opens up. With a rapidly growing economy, Vietnam has been at risk of power shortages as demand exceeds supply due to a lack of power infrastructure, and capital injections into the development of renewable energy could provide a good solution. Vietnam became the largest solar energy market in Southeast Asia in 2019, attracting foreign investors in mega plants in Binh Phuoc, Tay Ninh, and Ninh Thuan provinces, given the more attractive feed-in-tariff schemes compared to other countries in the region. Buyers have also been active with acquisitions of onshore and offshore wind farms in the central highlands and central coastal regions, which boast huge potential given their ample wind resources.
In Vietnam’s real estate market, M&A remains the quickest solution for foreign developers to enter the country and for local developers to expand their land portfolio. An increase in real estate M&A activity is expected this year, as various projects will be approved thanks to new improvements in the Law on Investment, after lengthy delays in the review process in previous years. Investors have accumulated a lot of capital, which is waiting to be deployed as the economy recovers, while owners struggling from the impact of the pandemic are willing to sell at lower valuations. Within the sector, industrial real estate has seen more activity in 2021, as multinational companies continue to shift their manufacturing bases from China to Vietnam despite the ongoing pandemic. Meanwhile, deal flow in residential real estate is expected to recover in the latter half of the year, as postponed transactions are resumed when travel restrictions are loosened.
Manufacturing, one of the sectors temporarily hit by Covid-19, will also provide opportunities to buyers who are confident of a strong economic recovery. Vietnam has been emerging as a manufacturing hub in the region given its low labor costs, its strategic location and many seaports nationwide, and its increasing participation in free trade agreements. For these reasons, its manufacturing sector will remain attractive to foreign investors, especially given ongoing China-US trade tensions, resulting in the relocation of manufacturing hubs from China to Vietnam. Domestically, there could also be a pickup in M&A activity, as we might see a trend in the consolidation of struggling small and medium-sized players into respective market leaders. Demand for growth capital from businesses looking for internal transformation and rebuilding post-pandemic will also present opportunities for investors looking for high-quality assets at attractive valuations.
Common risks and opportunities
Some of the common risks include uncertainty in the legal framework, especially new laws that came into effect recently, quality of information, as some companies still do not apply best practices in bookkeeping, an unfamiliarity among Vietnamese sellers with M&As and the basic concepts and processes involved, and cultural differences during deal negotiation and post-deal integration.
M&A transactions in Vietnam are largely governed by the Law on Enterprises, the Law on Investment, and the Law on Competition. Recent changes in these laws have posed additional challenges to potential buyers. For example, under the new Law on Competition, a substantially higher percentage of M&A deals are subject to merger control filing requirements, and the evaluation process could potentially add months of uncertainty to the timeline of a deal. Quality of information is also a common issue for foreign buyers, as target companies do not always have an organized information system that meets their requirements.
The current postponement of inbound international flights due to the pandemic also makes it difficult for buyers to conduct in-depth due diligence through site visits and face-to-face meetings. Additionally, foreign buyers might be unfamiliar with cultural differences in corporate governance practices in Vietnam. Many target companies are founder-owned, family-run businesses, which may not yet see the value-added of foreign strategic and financial partners or be open to international corporate governance standards. Last but not least, Vietnamese sellers lack knowledge in terms of how the M&A process works and is structured, which will create uncertainties.
Despite the existing drawbacks, it is important to acknowledge that compared to a decade ago, the perception of M&As in Vietnam has changed dramatically among government agencies, business owners, and investors/buyers and in a positive way. Authorities are continuously improving their turn-around times and responsiveness, while working toward new guidelines for M&A transactions, with the new Law on Enterprises, Law on Investment, and Law on Securities having come into effect on January 1, 2021. Shareholders are now more open to adding M&A as a strategic option in their growth trajectory and are becoming more educated in terms of M&A processes and key concepts. We see that sellers are taking a much more structured approach for large domestic deals or cross-border deals by engaging relevant advisors, who will help mitigate risks for foreign buyers by working with them through a transparent process. As BDA has a local team in Vietnam, we have been fortunate and pleased to be trusted by many local business owners and have given them advice and helped them run structured deal processes along the way.
We remain confident in the availability of opportunities in Vietnam’s M&A market. From a macro level value creation process perspective, Vietnam will continue to enjoy: (i) stable, unparalleled economic growth compared to other Southeast Asia countries, especially amid Covid-19; (ii) an influx of advantages from recent free trade agreements; and (iii) a strong government push to equitize State-owned enterprises. From a micro-level perspective, Vietnamese companies are becoming more professional with stronger management teams and better corporate governance. They are more open to foreign investors as they see the different values that both strategic and financial investors can bring.
Anticipated M&A deals and volume in next six months
Companies looking to position themselves for recovery in the post-pandemic economy will need new capital injections for internal transformation and further growth to remain competitive, and they will be eager to restart conversations with buyers for deals that were put on hold or lost. Within businesses in industries such as F&B, manufacturing, and industrials that have been negatively affected by the pandemic, there are still a lot of sizable and high-quality assets in the market. This environment will create opportunities for an increase in deal flow linked to dislocation, as sellers are more willing to close deals at a lower valuation in exchange for immediate access to growth capital. Until travel restrictions are loosened, local investors will have an advantage over foreign counterparts in such transactions, given their presence in Vietnam and their ability to run quicker processes and provide liquidity to businesses in need. We also expect to see a consolidation trend in M&A transactions, as market conditions have become challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with 25 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes. BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
Simon Kavanagh, Partner and Head of Industrials at BDA, shares his views on where we will see the most M&A activity within Industrials in Asia, in terms of sub-sectors, markets and key players in 2021 and beyond.
– Which are the most active sub-sectors in Industrials in Asia in terms of M&A activity since 2020?
There are two sub-sectors within Industrials where we’re certainly seeing a lot of activity. One is general component manufacturing, both metal components and plastic components. The automotive sector in particular has rebounded from a low in 2020, and we are seeing several deals in the marketplace currently. Component manufacturing then extends up into EMS and assembly, and there’s quite a lot of focus on electronic components, especially where there’s a technology angle.
The general trend for 2021 onwards is that technology is key. The R&D capabilities of target companies are scrutinized very closely by investors and the extent of their technology expertise has a meaningful impact on valuation. For pure play component manufacturing companies, with less of a technology angle, there is less demand, and appetite and valuations are lower.
Another sub-sector where we are starting to see increased activity is in waste recycling. This ties into the general mega theme towards ESG, which is becoming an attractive investment sector and one which funds and LPs are actively looking for opportunities.
– At the end of 2020, BDA closed a milestone transaction in the semiconductor sector with the sale of Compart to Shanghai Wanye. Compart is a leading global supplier of semiconductor components and assemblies, headquartered in Singapore with manufacturing plants in China and Malaysia. Do you see more opportunities in this subsector? Who are the most active investors?
The sale of Compart was a very successful transaction, for both buyer and seller. The investment environment is strong and there are several additional semiconductor related transactions coming to the market. BDA is currently working on a number of these, each in a different stage of the semiconductor manufacturing supply chain.
China has made it a priority to strengthen its domestic semiconductor capability and Chinese companies are keen acquirers. There is a strong willingness for Chinese corporates to borrow money and for private equity firms to commit capital to semiconductor related targets.
We expect the Chinese pace of investment in the semiconductor sector to continue for the next few years. It is an industry where most of the manufacturing and the technology is outside of China, either in Taiwan, Korea or the US. So there is a strategic value to the companies they are buying, even if valuation is relatively high. Private equity firms specialising in the semiconductor sector have sprung up. Wise Road Capital is one of the better-known ones: earlier this year it acquired MagnaChip in Korea for US$1bn. It was unusual for a Chinese company to buy something in Korea of that size, but it followed their 2020 acquisition of United Test and Assembly Center.
– How do you view the acquisition appetite of financial sponsors versus strategic investors for the Asian Industrials sector?
Financial sponsors have the upper hand at the moment and that will continue throughout 2021, until the macroeconomic environment stabilises and travel restrictions are lifted. The investor universe for industrial companies is weighted quite heavily towards Asian financial sponsors, with some activity and interest from Asian strategics. However, financial sponsors are much more flexible in terms of considering cross border M&A in the Covid-19 environment and being able to complete due diligence virtually.
Sponsor investors across the board are looking to increase their exposure to the region. Several international private equity firms have raised large Asia-only focused funds since 2020, including KKR, Blackstone and Carlyle. China-focused private equity firms (Boyu, Primavera, Fountainvest, BPEA, Hillhouse and PAG) are also investing or raising billion-dollar funds.
Strategic investors tend to be a little more conservative. It has not been a priority for US or European corporates to make significant investments in Asia these past couple of years: they have tended to focus on their home markets. The difficulty of doing site visits under the current Covid-19 travel restrictions has more of an impact on them, than on financial investors. However, while it is early stages, BDA is starting to see a change in the trend with a noticeable increase in the number of corporate clients calling us in 2021 to discuss buyside roles in Asia.
– China outbound M&A in 2020 was the lowest level in the last decade. Do you still see Chinese investors having a conservative view in outbound industrial deals in 2021?
The volume of China outbound M&A has come back from the low of 2020. Outbound volume in Q1 2021 was up 15.9% YoY. But in general, yes, the heyday of Chinese outbound diversification has gone. US assets are still out of favor due to geopolitical tensions. Europe is attractive, but acquirers are far more cautious, both in terms of what they buy and how much they pay for it.
When they do make acquisitions it’s the technology that is most critical. China’s next stage of development is very much towards being at the forefront of technological leadership and R&D capabilities. They are looking at what this target can bring to them in the industry. Does it have something that is not essentially in China already? What can a new Chinese owner do to win Chinese customers for this foreign company? Does the target company have some special intellectual property or is it the leading expert in a particular niche? Technology will remain the key driver for outbound M&A for many more years.
– SPACs have been a hot topic recently. What impact do you think SPACs will have on the industrial sector in Asia?
Not much of an impact. SPACs tend to focus on high growth companies that are looking at raising capital and want to do an IPO, but are less suited to the more traditional routes for public listing. There are not many industrial companies that fall into that category. Local Asian SPACs are still not regulated or available / approved by regulators in either Hong Kong or Singapore, although that will change in due course. In order to pursue the SPAC route in either the US or Europe, the business needs to be big, like Grab. But if you’re a US$1 billion valuation Industrials company, you won’t need to sell new shares to raise capital, and if you’re looking for liquidity you will probably just go and do a normal route IPO or sell to a financial sponsor.
– Is the shift of manufacturing capacity to Vietnam, at the expense of China, continuing?
Yes, the trend will continue for the foreseeable future. Vietnam still has a significant cost advantage over China, particularly for labor-intensive industries. Companies are not necessarily moving their entire supply chain from China to Vietnam, but if they are adding capacity, it’s less likely that they will be making that capital expenditure in China. Vietnam, as well as Malaysia to some extent, are continuing to benefit because of their well-qualified workforce of engineers and a friendly FDI regulatory environment.
With our strong BDA Partners team on the ground in Vietnam, we are seeing and working on a lot of founder-owned sellside transactions where the target companies are very attractive bolt-on acquisitions for strategic investors. We’re witnessing the start of a shift, where a generation of founders of some very successful Vietnamese companies are looking for liquidity, and they need access to an international investor universe and an advisor to help guide them through an M&A process.
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with 25 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes. BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
SPACs are the hottest story in financial markets globally, today.
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (“SPACs”) have been around for 30 years, but they blossomed in 2020, in the US market. 248 SPACs launched last year, raising a total $83bn in proceeds.
And the craze keeps getting hotter: in January and February 2021 alone, 188 SPACs raised $58bn, just in the US.
This rising tide shows that the SPAC approach is, for now, seen as a legitimate and quicker alternative to a traditional US IPO. And yet SPACs are in favour and controversial for the same reason: highly favourable economic returns to SPAC IPO sponsors, market challenges caused by the pandemic, and the apparent execution, pricing and liquidity certainty offered by SPACs, for both investors and target companies.
Today, 300 SPACs are searching for acquisition targets to de-SPAC within a limited timetable, typically two years. As the US becomes saturated, SPACs are increasingly looking for opportunities in South East Asia and Greater China, where companies backed by private equity and venture capital are demonstrating compelling growth and value prospects.
Total deal value of Asia-focused SPACs (US$bn)
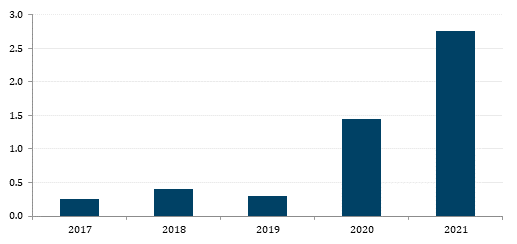
This year, we’re beginning to see Asian sponsors listing SPACs in the US.
And yet only two Asian countries, South Korea and Malaysia, allow SPACs to list today.
SE Asia is arguably the most fertile ground for acquisitions by SPACs, due to the vibrant technology startup scene and smaller domestic IPO markets. This raises the question of whether financial hubs like Hong Kong and Singapore should themselves consider becoming more SPAC-friendly.
But for now, Asian companies are mostly looking to SPACs in the US.
Here are some of the ways Asian markets are engaging with SPACs – or resisting them.
1. CHINA
China is the go-to model for the South- and SE-Asian technology unicorns. Alibaba and JD.com are Chinese giants with dual US-China listings. Political pressure and rampant local multiples have encouraged Asian companies to explore regional markets, not just NASDAQ.
Notwithstanding the trade war, NYSE and NASDAQ have expressed willingness to continue to entertain China-related SPACs.
US billionaire Dan Och and his family office, Willoughby Capital, own 5.6% of Primavera Capital Acquisition Corp, a SPAC led by Fred Hu, formerly of Goldman Sachs China, hunting for a consumer target with a significant presence and potential in China. Primavera raised $350m in an NYSE IPO.
Fang Fenglei, founder of HOPU, is active via HH&L, a SPAC, now chasing a China healthcare target.
CITIC Capital raised $240m for a SPAC targeted on the energy efficiency, clean technology and sustainability sectors, in China and beyond.
The Shanghai Stock Exchange’s Sci-Tech Innovation Board (STAR Market), has attracted many high-growth startups. The popularity of these platforms offers issuers potentially stratospheric valuations, without going down the SPAC route.
New Frontier Group, an asset manager run by Anthony Leung, Hong Kong’s former financial secretary, merged Chinese private hospital United Family Healthcare with its SPAC on the NYSE in 2019. New Frontier Health is still trading below its $10 IPO price, and is soon set to be taken private by a consortium, again led by Leung, valued at only $12 a share.
Octillion Energy, a privately-held US and China headquartered electric vehicle powertrain solutions provider recently hired Bank of America to explore a potential acquisition by a NASDAQ listed SPAC instead of a trade sale.
2. HONG KONG
Hong Kong and Singapore are taking divergent approaches to the SPAC boom, as they watch Asian unicorns explore future listing structures.
The Hong Kong Exchange prefers traditional IPOs and is treading a more cautious path.
Hong Kong has long been one of the world’s top IPO destinations alongside New York and Shanghai, and it has been skeptical about non-IPO listings. In recent years, HKEX has been tightening rules on backdoor listings and shell activities. Regulators in Hong Kong and mainland China have been working hard to streamline and simplify conventional IPO listing procedures and requirements, reducing the appeal of the SPAC route. Hong Kong already allows pre-revenue biotech companies to list on its main board.
Model Performance Acquisition, a Hong Kong-based blank check company led by ex-Templeton Asset Management North Asia PE co-head Claudius Tsang, has filed with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to raise up to $50m in an IPO.
Ace Global Business Acquisition is a Hong Kong blank check company targeting gaming and e-commerce in China, Japan and SE Asia, launching a US IPO. The company is led by Eugene Wong of Whiz Partners Asia and the China Hero PJ Fund.
HKEX’s CEO Calvin Tai said the bourse “will open our eyes and ears, listen to the market, and watch other markets” when it comes to future IPO regulations.
In 2020, 154 companies raised a combined US$52bn in IPO proceeds in Hong Kong.
3. INDIA
An array of Indian companies, valued at $30bn or so in total, are considering SPAC deals in the US. For example, Indian ecommerce pioneer Flipkart, owned by Walmart Inc, is mulling merging with a blank-cheque company in the US, potentially at a $35bn valuation.
SPACs are scouring India’s more mature targets. Last week, ReNew Power, one of India’s largest renewable energy groups, unveiled plans to go public in New York through an $8bn deal with a SPAC. ReNew Power is an Indian renewable energy company, with an asset base of 8 GW, of which 5 GW is operational. It is now exploring a dual listing in Mumbai.
Baring Private Equity Asia is considering listing US-Indian health tech company, Citiustech Healthcare Technology Pvt., in the US through a SPAC merger. Baring is hoping for a valuation of US$1bn for Citiustech. Baring only acquired its majority stake in Citiustech in 2019 for US$750m.
4. INDONESIA
Indonesia is a less mature market, but with a huge consumer population and a growing online economy. This has created four unicorns to date. Naturally they have considered the merits of listing via SPAC.
The Indonesia Stock Exchange is the third Asian market, after Hong Kong and Singapore, to consider allowing SPACs to list. Last year, there was only one SPAC deal involving an Asian company. Only five Asian start-ups have listed via SPAC since 2016.
Ecommerce leaders Tokopedia and Bakalapak, and airline ticketing and hotel booking services player, Traveloka are all considering SPAC mergers today. SPAC deals may be just one step along the way: a proposed $18bn merger between Tokopedia and ride-share giant Gojek could lead to a dual listing in New York and Jakarta.
The biggest SPAC focused on SE Asia is Bridgetown Holdings, backed by Richard Li and VC Peter Thiel. Bridgetown raised $595m, and is exploring a potential merger with Tokopedia that could value the unicorn at $8bn-$10bn.
Provident Acquisition is a $200m SPAC launched by SE Asian fund Provident Growth. Provident backed Gojek, Indonesia’s biggest start-up, and Traveloka.
5. JAPAN
Japan doesn’t allow SPACs on its domestic markets. The Japanese authorities don’t consider SPACs to be sufficiently transparent or safe in regulatory terms, as a path to IPO, or as an investment vehicle.
SoftBank is listing two new SPACs on NASDAQ. The Japanese conglomerate will raise $480m to acquire businesses in the AI sector. SoftBank’s SPACs are funded primarily by its Vision Fund. SoftBank listed its first SPAC in the US in January 2021, raising $525m.
6. SINGAPORE
The Stock Exchange of Singapore is likely to approve the formation of SPACs in Singapore.
Singapore’s IPO ranking is far behind Hong Kong, while it has suffered a slow-burning delisting trend in recent years – making it more receptive to SPACs as a growth engine.
The Singapore Stock Exchange is home to more old economy companies and REITs. SPACs would be a natural step for Singapore to attract new economy listings.
The spectacular rise of Sea, the Singapore gaming and ecommerce company listed on NYSE, was one of the world’s best-performing stocks in 2020.
Grab, backed by SoftBank and Shinsegae, is exploring going public in the US through a merger with a SPAC to speed up its listing process. Grab is a “super app” that offers multiple conveniences, including ride-hailing, financial services and food delivery. The platform has traction in eight countries — including Singapore, Indonesia, Vietnam and Thailand. Its mobile app has been downloaded more than 14 million times. This comes after talks to combine with Indonesian rival Gojek collapsed. See above.
Singapore’s on-demand bus service provider Swat Mobility is contemplating a Japan IPO to fund its expansion, or else a merger with a US SPAC to gain a listing there.
COVA Acquisition, Crescent Cove’s $300m SPAC, listed in February, is now scouting for targets across SE Asia.
L Catterton Asia Acquisition Corp launched this week as a consumer tech-focused $250m IPO on NASDAQ.
SPACs formed in 2021, searching for targets in Asia
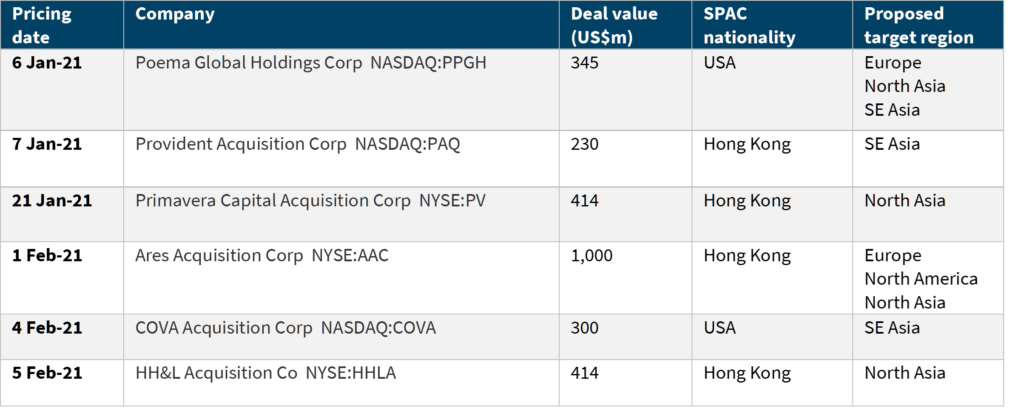
Source: Dealogic, Mergermarket
Investors have already poured almost $3bn into SPACs focused on acquiring Asian companies this year, nearly doubling the amount committed during all of 2020, according to Dealogic. While modest by the standard of American companies, BDA understands that several Asian private equity firms are hoping to join the stampede.
The gold-rush mentality is causing concern from sponsors looking to invest, about inflated valuations for young businesses. Asian management teams at fast-growing companies are typically unprepared for the regulatory requirements of a US listing. Asian markets are simultaneously tightening restrictions on backdoor listings which avoid the independent due diligence process on a traditional IPO.
As described above, many of Asia’s most high-profile entrepreneurs and CEOs are playing in the SPAC pool. In addition to Fred Hu, Ken Hitchner, ex-head of Goldman Sachs Asia Pacific, Li Ka-shing’s son Richard Li, and Peter Thiel, the US tech investor, have all backed significant SPACs focusing their aim on SE Asia.
Most of SE Asia’s burgeoning unicorns are still valued below $3bn, which was the traditional minimum value for an IPO in the US.
As a result, Asia-focused SPACs are chasing a limited pool of viable targets.
However, Asia’s limited history of companies successfully going public via SPAC could weigh on the region’s prospects.
Sponsors have also come under scrutiny for their own lucrative compensation, typically a 20% stake in the company.
They have flocked to the US, where investors show apparently limitless appetite for blank check firms, while the larger exchanges in Asia still do not allow SPACs to list.
SPACs feel like a reflection of the mature bull market. The exuberance has sparked debate among investors and bankers about how long the trend will continue, and whether there will be enough suitable targets to be merged, if the frenzied pace of fundraising continues.
Many observers expect the SPAC mania to end badly – but not before more investors, CEO, bankers and sponsors have ridden the wave for a while longer.
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with 25 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes. BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
We spoke to Huong Trinh, Managing Director and Head of the BDA Partners Ho Chi Minh City office, about the latest exciting developments in M&A in Vietnam.

You worked on the largest inbound private sector industrial transaction in Vietnam in the last three years, the sale of Thipha & Dovina to Stark Corporation, for US$240m. Why were Thipha & Dovina such an attractive investment opportunity for an international buyer?
Thipha & Dovina are a leading electric cable and non-ferrous metal group with a 30-year history. The companies grew revenues at an average 20% per annum for the period 2015-2019, and revenue exceeded US$500m.
This asset offers direct exposure to Vietnam’s economic growth. Vietnam has been emerging as a manufacturing hub in the region given its relatively low labor cost and strategic location. In 2019, Vietnam recorded GDP growth of ~7%, and is expected to remain a regional outperformer. Significant investment in infrastructure is underway. The government and business led spending will drive demand for cable and wiring for the foreseeable future.
Thai buyers are consistently interested in Vietnamese assets, and have made several significant investments in Vietnam over the last few years.[1]
Do you think there will continue to be inbound interest in Vietnamese companies from the rest of Asia and further afield in the future? If so, what are the key reasons?
Obviously yes, as we have received lots of indications of interest for high-quality industrial assets, as well as other sectors, from both global and regional buyers. We believe the strong inbound interest is mostly driven by the following factors:
- Vietnam’s economy is driven by consumer spending, which accounts for close to 70% of its GDP. With the third largest population in ASEAN, and the expansion of upper and middle-income earners, the economy is expected to grow further. Despite the disruption from COVID-19, Vietnam is expected to still enjoy ~3% economic growth this year and is expected to bounce back to 6% growth in 2021[2]
- Vietnam will benefit from recently signed Free Trade Agreements (CPTPP & EVFTA), which encourage more foreign direct investment into the country and put in place lower tariff structures. This is also an indicator of strong EU-Vietnam relations
- Vietnam has been emerging as a manufacturing hub in the region given its relatively low labor cost, but with increasing quality and a strategic location with many seaports nationwide. Global companies started shifting operation to Vietnam in 2010, and this trend has been accelerated by the ongoing US-China trade tensions
Are there opportunities in Vietnam for BDA to sell founder owned businesses in the future?
We believe there are still many more opportunities in Vietnam to advise founders on the sale of their businesses in the short term. There are still a lot of sizable and high-quality assets in the market that have grown into market leaders over the course of several decades and which have undergone different phases of development. They may need a new “growth engine” or investment to remain competitive and in some cases the founders are simply looking to exit and step back from the company they founded.
In addition, improved legal framework and corporate governance are making it easier and more transparent for foreign investors, giving them greater confidence to acquire majority stakes.
We are currently mandated on a number of projects thanks to: (i) a combination of our strong relationship with both strategic and financial sponsor buyers because of our global network; (ii) a senior team on the ground in Vietnam (especially important during COVID-19); and (iii) excellent execution capabilities which are laser-focused on delivering the best outcome for our clients.
Which will be the most attractive sectors in Vietnam for M&A in the post COVID-19 environment and why?
Internet-related businesses have been growing rapidly during COVID-19. Online, or online-to-offline, products and services have seen significant growth. This is not just a short-term effect; consumer behaviour is changing, and this is a long-term sustainable shift in consumer dynamics. Average order value on e-commerce sites rose by over 35 percent year-on-year in the first half of this year.
People are still spending money on shopping, a good sign given the fears that demand would fall during the COVID-19. The best performer was the groceries and fresh food, following by household supplies, homecare and healthcare products. Shopping malls are now packed with people like COVID-19 was never here.
For the industrials sector, COVID-19 has been certainly a catalyst for business owners to consider a transaction. The underlying reason was the fundamental change in the economic outlook domestically and globally, which has urged a number of investors to look for a more stable and “safer” destination whilst business owners see the benefits of having a “big brother” who is financially strong together with them to grow the business, especially during the unstable periods.
Healthcare is another attractive sector for investors. Some of the healthcare sub-sectors are performing well during COVID-19, while some are not. The sector will likely see lower cash flow in 2020 compared to 2019. Hospitals face a huge negative impact on revenue as they have had to cancel many profitable surgeries and procedures, while spending more on staffing and getting extra protection equipment for work. In contrast, personal protective equipment companies are seeing significant revenue growth, and the pharmaceutical sector will continue to grow strongly post pandemic.
Industrial real estate and logistics will also grow, thanks to multinational companies shifting their manufacturing base from China, and the requirement for logistics and supply chains to keep up.
Sectors that have been temporarily hit by COVID-19, such as food & beverage, hospitality and discretionary retailing, present opportunities at attractive valuations for buyers who are confident of a strong bounce back after COVID-19.
Do you see any changes in perception towards M&A processes in Vietnam? Have handshake deals been completely replaced by more structured processes?
Compared to a decade ago, the perception towards M&A has been changed drastically among business owners, government agencies and investors/buyers in a positive way. As Vietnam’s economy has opened up, we have witnessed more and more large deals that have brought positive growth to the target companies and benefits to all stakeholders. As awareness of the positive benefits of M&A has grown, shareholders are now more open to adding M&A as a strategic option in their growth trajectory and strategy. Sellers are becoming more educated in terms of an M&A process and key concepts. I still remember 15 years ago, it took me a lot of time to explain to the business owners how investors would value a business, which was not only based on how many land use rights the company held or how famous their company was.
For small deals, or deals between two domestic parties, handshake deals are still common, with all the decisions being made quickly, top down. However, we see people are taking a much more structured approach for medium and large domestic deals or cross-border deals. These deals will involve a variety of advisors as shareholders see the benefits of having an official process and professional advice: (i) better positioning the company; (ii) consistent and organised approach; (iii) a more competitive process will result in better equity valuation and terms; and (iv) increase the certainty of the deal completing and reduce the associate deal risks.
As BDA has a local team in Vietnam, we are happy to be trusted by local business owners to give them advice and help them to run a structured M&A process.
How do you see international investors completing transactions with Vietnam’s borders still shut?
BDA has signed and/or completed three transactions so far in 2020 without the buyers coming into Vietnam for the closing/signing.
This was a key concern when COVID-19 started, but as things have progressed, it is really a matter of how much both sides like the deal and how we, as the advisor, add value. We have been very creative with our sale processes. For example, helping the investor hire a local advisor to do the site visit/management meeting on the ground in Vietnam; arranging for the seller to take high-quality videos of the factories and assets, and so on. These creative approaches help to get deals done.
According to the AVCJ, 2019 was a record year for the number of PE / VC investments in Vietnam. Do you expect to see a rise in domestic and international private equity investment in Vietnam continuing in 2020 and 2021?
From a macro level value creation process perspective, Vietnam will continue to enjoy: (i) stable, unparalleled economic growth compared to other Southeast Asia countries, especially amid the COVID-19 situation; (ii) an influx of advantages from the recent free trade agreements; and (iii) strong government push to privatize state-owned enterprises. From a micro-level perspective, Vietnamese companies are getting more professional with stronger management teams and better corporate governance. They are more open to foreign investors as they see the different values that both strategic and financial investors can bring to the companies.
There is increasing demand for growth capital in 2020-2021. The private sector in Vietnam, with its strong momentum, will need more capital to pursue transformational changes and achieve further growth. The start-up ecosystem is seeing robust expansion, with internet related companies as the most attractive sector.
We, at the BDA Partners Ho Chi Minh City office, are seeing strong demand for growth capital and exits from both founder-backed and private equity owned companies. This is visible from our numerous live deals and strong pipeline/opportunities for 2021.
Contact us for more details on the insights
[1] In 2014, Berli Jucker Pcl announced a US$879m transaction to acquire Metro Cash & Carry Vietnam. In 2015, Central Group through its subsidiaries, Power Buy, bought 49% stake in Nguyen Kim Trading Company. In 2016, Central Group acquired Big C Vietnam, a supermarket chain, with a transaction value of US$1.0bn. In 2017, ThaiBev Group, through its subsidiary Vietnam Beverage, has acquired majority stake in Sabeco, Vietnam’s largest brewery company, with a deal size of US$4.8bn. SCG, a Thailand conglomerate, has done a number of transactions in construction materials and packaging in Vietnam.
[2] HSBC research shows Vietnam enjoying very strong internal domestic demand even during COVID-19. Nielsen research indicated that Vietnamese consumers remain 2nd in ASEAN in terms of being positive.
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with over 24 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes.
BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
Originally published as an op-ed in the Barron’s
In the 1990s, financiers used to mock “the FILTH”: British bankers or business people who “fail in London, try Hong Kong.” If you couldn’t make it anywhere else, you could still make it om the shores of the fragrant harbor whose ever-rising tide floated all boats. Hong Kong was the Manhattan, Las Vegas, and Los Angeles of Asia, all rolled into one—money, nightclubs, fast cars, world-class restaurants, stock-market booms, beaches, yachts, and dodgy go-go bars. It was a boomtown because it was the gateway to China. This was the staging post for the greatest gold rush of the 20th century: the reawakening of the Chinese dragon. Despite the recent crackdown on civil liberties, Hong Kong is far from turning into a financial backwater. As long as opportunity still exists, it will continue to attract foreign investors who feel more at home there than on the mainland.
Expats have long preferred Hong Kong to Shanghai or Beijing. The city boasts better schools, hospitals, and espresso bars. Google still works. Unlike on the mainland, business and society has felt free. While the British had never granted Hong Kong true democracy, the rule of law was clear. Private-equity firms enjoyed a fairly level playing field, taxes were low, the press was free, and the judiciary was independent. That’s why Britain fought so hard for the principle of “one country, two systems,” which was enshrined into law, for 50 years, when Hong Kong reverted to Chinese rule. China promised to give Hong Kong the democracy that Britain had denied its colony. Of course, the truth has emerged rather differently.
Suddenly, Hong Kong is out of fashion. Riots, the Covid-19 pandemic, and Chinese government repression have combined to scare away those same expats who made it their home. Six weeks ago, China imposed a broad national-security law on Hong Kong banning secession, subversion, and collusion with foreign countries. It’s already having a dramatic effect on the city’s media and politics. The new law eliminates civil rights that local residents have long exercised, and raises the specter of foreign business people being arrested for vaguely defined offenses and being deported to stand trial in China.
Beijing, far from liberalizing, is cracking down on dissent inside and outside its borders. The new security law explicitly applies beyond Hong Kong and covers non-Hong Kong residents, making this once freewheeling city dangerous for anyone viewed unfavorably by Beijing. Growing economic tensions between the U.S. and China have also led to tariff and nontariff barriers.
Last week, more than 200 police officers raided the head office of Apple Daily, the city’s most-read pro-democracy newspaper. Several managers were arrested, including the paper’s high-profile, millionaire owner, Jimmy Lai. Lai faces an array of charges, notably collusion with foreign countries, under the new law. He has a good relationship with the Trump administration and has testified before Congress in the past.
At the same time, China is trying to reassure the world that it should still do business with Hong Kong. For the foreseeable future, the city will still be the hub for inbound and outbound mainland investment. While Singapore has gained traction with private-equity professionals, boasting a transparent legal framework and increasingly broad tax treaty, Hong Kong is countering with incentives of its own. A new Limited Partnership Fund Bill hopes to establish Hong Kong as a prime Asian destination for private-equity and venture-capital funds. The legislation proposes Hong Kong as a domicile for private equity, venture capital, and real-estate funds and will attract private funds and family offices to Hong Kong. Domiciling in Hong Kong would give these firms direct access to the region and to Hong Kong’s robust capital markets. It will be a catalyst for growth in tech and financial services.
Officials have also announced plans to introduce a new carried-interest tax scheme, expected to be one of the world’s most liberal, intended to make the city a viable alternative to the Cayman Islands, especially for Asia-focused funds. The Hong Kong government is also planning to provide extensive tax concessions for private-equity funds’ “carried interest” performance fees. Singapore offers similar advantages, but Hong Kong is aiming to be even more generous to investors.
All of this will be attractive to investors as Hong Kong is still swimming in wealth. Tycoons have outperformed almost everyone else. With a population of only 7.5 million, the territory ranks seventh in the world with 96 billionaires and a combined wealth of $280 billion, according to Wealth-X’s Billionaire Census 2020. Of all world cities, only New York can boast more billionaires.
Hong Kong is clearly now part of the People’s Republic of China and, prompted by the government, mainland money is pouring in,but there’s little sign of foreign capital fleeing. Foreign investors who want to share in China’s economic growth have little choice but to use Hong Kong’s capital markets as their main vehicle. The Hong Kong dollar has held its trading band against the U.S. dollar. The stock market has seen heavy inflows from mainland institutions, and there are more and more “red-chip” companies, based in mainland China, but listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. The Hang Seng Index fell sharply in the first quarter but has recovered 14% from its March low. The index is still 9% off its peak from two years ago, yet rumors of Hong Kong’s demise may be exaggerated, or just plain wrong.
Even though China has put a harness around the neck of its golden goose, Hong Kong’s economy is too precious to kill. Vietnam and Singapore are certainly benefiting from Hong Kong’s recent woes as expats move in and fund managers direct more money into those markets. Still, as long as Hong Kong’s financial advantages remain, Western professionals and investors may find themselves back in the gleaming office towers of Hong Kong Central quicker than they expect.
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with over 24 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes.
BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
BDA Co-Founder and Senior Managing Director Charlie Maynard talks about opportunities in the Asian M&A market and how BDA runs an excellent sellside process and delivers the best results for clients.
In this working-from-home chat with BDA senior leadership, we talked to Charlie Maynard. Charlie co-founded BDA Partners with Euan Rellie 24 years ago in Singapore and New York. He has spent many, many years in different countries in Asia before and after founding BDA. We talked about the opportunities he sees in the Asia M&A market, and how BDA runs excellent sellside processes and delivers the best results for clients.
What opportunities did you see in the Asian market when setting up BDA in 1996?
We realised that there was a gap in the market, because the big banks were talking about being interested in global M&A and how important Asia was to them, but in reality they were much more focused on Western M&A and Chinese IPOs, where the big bucks were. While we understood that Asian M&A was a tough market, but we reckoned we could build a business by entirely focusing on it.
How has BDA evolved over the years?
When we started out in 1996, we were largely a buyside shop, working for large, primarily Western MNCs looking to acquire in Asia. The buyside work was very useful in terms of helping us understand sectors and what clients wanted. For the first ten years of BDA, the sellside market and particularly the private equity buyout based sellside market didn’t really exist. But around 2006-2007 there were signs that it was beginning to take off, and that was when we made the switch to focus on the sellside which is 80% or more of our business today.
The other two big changes were a few years back when we started both to build out and focus on our six core sector expertise including Industrials, Chemicals, Health, Technology, Consumer & Retail and Services as well as to set up a dedicated financial sponsors group coverage team which would focus full time on our relationships with sponsors.
How are BDA set up to deliver the best results for clients?
To run excellent sellside deals, you need to have global reach in order to access all buyers and be agnostic as to where the buyer comes from. There are very few parties that can really access all relevant buyers, regardless of geography, and why this business that we’re selling is attractive. We are one of the very few M&A advisories who can do that.
You also need to have the sellside process nailed. We are very, very process oriented. We systemize and automate the basic bits of a sellside process, which are normally repetitive, so we can focus on the difficult, critical bits which are specific to individual transactions and help our clients as fully as possible by adding real value. This is another key differentiator that we have in terms of systems and processes compared to our peers and competitors.
What can we expect from BDA Partners for the next five years?
If you do M&A, you want to be doing sellside M&A. The growth in the buyout market over the last 5- 10 years has been enormous in Asia. And if you look at the capital that has been raised over the last 1-3 years, it’s clear what we have seen to date is only a fraction of what we are going to see in the future. It’s a huge and rapidly growing market, but because of the complexity and global reach required, there are very few advisors that can effectively service this market. Sellside M&A advisory will remain our core business and we’ll continue to focus on raising our deal size.
Beyond that, we started to get involved in debt advisory and restructuring by a partnership with Zerobridge, as well as trying out principal investing with BDA Capital Partners. There are quite a lot of exciting opportunities for other avenues of growth in addition to the core M&A business.
What have been the biggest challenges in BDA’s journey so far?
The hardest challenge has been creating the global network we have today, where each person in each office can deliver much more than they are able to do individually. This has taken a lot of time and it is completely and utterly about the people inside BDA. It’s ever evolving and must always be improving and progressing through our team efforts. Keeping the team moving forward and focused across nine different offices and 12 different time zones will always be challenging.
What are you most proud of about BDA?
It is the team that has created this seamless global network that allows us to deliver the best results for our clients. I love our team and I love our team spirit. Very, very few organisations have as diverse and international a team which truly works together in a fast, coordinated and intelligent way. I love the fact that we have so many people from so many countries liking each other and enjoying working as a team – and that this teamwork delivers great results.
Latest insights from BDA
- Software in Asia
- China Healthcare M&A outlook for 2024
- HealthTech sector landscape
- M&A trends and outlook for 2024
- Cooling-as-a-Service: Decarbonisation by Servitisation
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with over 24 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes.
BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
While there has been broad discussion on how businesses and markets have responded to the coronavirus outbreak and how they will adapt to a post COVID-19 world, arguably, no industry has received as much attention as clinical diagnostics. With the heightened focus on testing, terms such as antibody test and nasopharyngeal swap have jumped from medical journals to the front pages of newspapers the world over.
Thanks to previous experience with SARS, Asian IVD companies in many cases have led innovation in combating SARS-CoV-2. Regulators worldwide are closely studying the rapid response and mobilization of testing resources seen in China and Korea at the outset of the pandemic. However, even with the situation stabilizing in East Asia, companies in the region continue to innovate – developing more rapid point-of-care tests and antibody testing platforms, not to mention the urgent research into a possible vaccine being led by companies like CanSino and Shenzhen Geno-immune in China, Bharat Biotech in India, SK Biopharma in South Korea, and Takeda in Japan, to name only a few examples.
While the response to the pandemic has lifted the valuations of diagnostic tools and technologies companies globally, Asian companies have been trading, on average, at over 30x trailing EBITDA, led primarily by premium valuations achieved by Chinese diagnostic tools companies. We expect the spike in valuations will create opportunities in the space and accelerate consolidation efforts in the region, especially in China where the IVD market is less concentrated and the rise of import substitution in the diagnostic products space has attracted increased investment from both healthcare companies and firms in other industries looking to capitalize on the trend.
While year-to-date M&A activity has been muted across all industries, BDA and our partners William Blair continue to participate in deal activity in the diagnostics space, including the recently announced sale of FountainVest’s stake in Chinese IVD business Shanghai Kehua Bio-engineering in China and the sales of Stratos Genomics to Roche and of Exalenz to Meridian Biosciences in the US and Israel, respectively. We have also seen significant capital markets activity in the diagnostic tools and technology space so far this year.
In many ways, the coronavirus pandemic has accelerated a growth trend already taking place in Asia. Thanks to a focus on preventative care to reduce healthcare costs and the increasing prevalence of diagnostic testing, the Asian IVD industry had been poised to achieve double-digit growth over the next five years, even before the first cases of COVID-19 were reported.
While it could be argued that the impact from COVID-19 on the diagnostics space will be short-term, BDA has seen an interesting dynamic emerge where demand for more routine test kits, such as flu tests, have fallen due to COVID-19. We expect this will be temporary and not dampen mid-term demand. If anything, the pandemic has triggered increased spending on development that will spur further innovation for years to come.
Download the full report
Contact BDA healthcare team
- Andrew Huntley, Senior Managing Director, Asia/Europe: ahuntley@bdapartners.com
- Lei Gong, Managing Director, Shanghai: lgong@bdapartners.com
- Kumar Mahtani, Managing Director, Mumbai: kmahtani@bdapartners.com
- Peter Moreno, Vice President, New York: pmoreno@bdapartners.com
Related content
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with over 24 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes.
BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
Since the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak in December 2019, it’s become evident that the disruption to the economy will impact not just China but the rest of the world. Obviously, there is still a lot of uncertainty about what will happen –but the effects are already dramatic. Major cities are locked down. A mass quarantine of tens of millions of people. Millions are stuck and banned from travelling in and out of China. Thousands have died.
Businesses are taking drastic measures. Thousands of Chinese factories are yet to reopen. Tens of millions of professionals are working from home or on rotation. Students are on extended breaks.
Global airlines have mostly suspended flights to China. Travel and visa restrictions have been established in almost 100 countries.
The global supply chain has been disrupted. Countless businesses have been impacted by the outbreak of the coronavirus.
Not surprisingly, demand for most discretionary goods has dropped dramatically across the region. Tourism, hotels and airlines are decimated. Retail stores and restaurants are in deep trouble. Consumer staples such as groceries, rice, instant food and toilet paper have remained resilient. The epidemic has helped supermarkets and e-stores attract new online customers without extensive marketing and promotional efforts.
Some sectors might benefit from the virus outbreak –but not most. Anything that is related to digital, direct-to-consumer, healthcare: online supermarket, food delivery, digital home entertainment, online games, online education, healthy foods, consumer health and drugs, will benefit.
Surgical masks, alcohol sanitizers and other hygiene products are the most obvious beneficiaries of the coronavirus disruption.
We think the coronavirus outbreak will accelerate the shift towards online shopping and entertainment, boosting online segments. The new O2O, ecommerce delivery model fits well with consumer needs when they are asked to stay at home. The new habits people pick up in the next few months will last, in many cases, forever.
We saw US$40bn in global lost productivity due to SARS in 2003 and US$55bn during the 2009 H1N1 swine flu pandemic, both of which involved China. Those numbers could be dwarfed by this new virus –which could delay growth of hundreds of billions of dollars.
Global growth will resume as long as the coronavirus doesn’t last too long. Three lost months will be a big hit. Six lost months could mean some countries tip into recession. It is too early to assess how big the impact is, but we are impressed by a sense of calm and resilience by financial players.
Q1 profitability will be negatively impacted globally. M&A deals will slow down dramatically in the next couple of months. Valuations may drop in the short term but should bounce back sharply. Post-virus, there will be pent up demand, from delayed consumer discretionary spending, and delayed spending on consumer durables. We expect deals to rebound once the virus is contained. In the meantime, there will be good buying opportunities in China and beyond.
Contact the BDA Consumer & Retail team
- Euan Rellie, Senior Managing Director, New York: erellie@bdapartners.com
- Karen Cheung, Managing Director, Hong Kong: kcheung@bdapartners.com
- Vivian Ren, Managing Director, Shanghai: vren@bdapartners.com
About BDA Partners
BDA Partners is the global investment banking advisor for Asia. We are a premium provider of Asia-related advice to sophisticated clients globally, with over 24 years’ experience advising on cross-border M&A, capital raising, and financial restructuring. We provide global reach with our teams in New York and London, and true regional depth through our seven Asian offices in Mumbai, Singapore, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seoul and Tokyo. BDA has deep expertise in the Chemicals, Consumer & Retail, Health, Industrials, Services and Technology sectors. We work relentlessly to earn our clients’ trust by delivering insightful advice and outstanding outcomes.
BDA Partners has strategic partnerships with William Blair, a premier global investment banking business, and with DBJ (Development Bank of Japan), a Japanese government-owned bank with US$150bn of assets.
US securities transactions are performed by BDA Partners’ affiliate, BDA Advisors Inc., a broker-dealer registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). BDA Advisors Inc. is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and SIPC. In the UK, BDA Partners is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In Hong Kong, BDA Partners (HK) Ltd. is licensed and regulated by the Securities & Futures Commission (SFC) to conduct Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities to professional investors. www.bdapartners.com
